Week 7/31: NoSQL and Vector Databases for Data Engineering Interviews
Understanding NoSQL and Vector Database Practices in Data Engineering
As Data Engineers, working with NoSQL databases is crucial to managing modern data systems, especially when dealing with large-scale, distributed, or real-time applications. NoSQL databases are invaluable for handling unstructured or semi-structured data, offering flexibility and scalability tailored to diverse project requirements.
In this post, we will cover the following topics:
What is NoSQL?
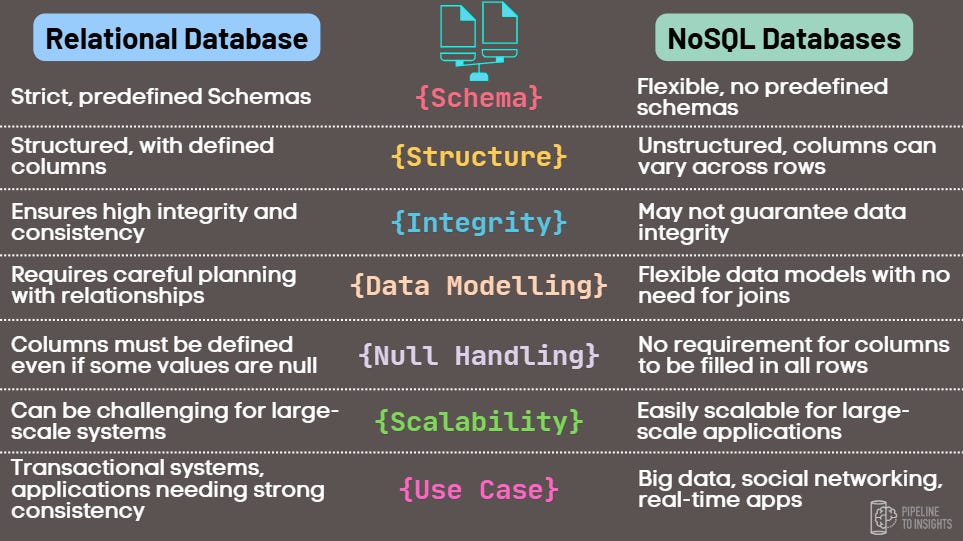
The differences between Relational and NoSQL Databases.
The various types of NoSQL databases including definitions, use cases, and examples.
Common interview questions related to NoSQL.
Additionally, we will discuss Vector Databases, which are becoming increasingly relevant in interviews, particularly for roles closely related to AI Engineers and ML Engineers.
For the previous posts of this series, check here: [Data Engineering Interview Preparation Series]1
What is NoSQL
NoSQL, short for "Not Only SQL" emerged in the early 2000s to meet the needs of modern web applications. It's designed to provide speed, flexibility, and scalability, working alongside traditional SQL databases rather than replacing them.
Relational databases are excellent for ensuring data integrity and consistency, but they fall short in flexibility and scalability. These systems rely on fixed schemas and scale vertically by upgrading hardware, which becomes inefficient when handling large volumes of data, such as in applications with millions of users.
NoSQL databases address these challenges by enabling horizontal scaling, which distributes data across multiple computers. They also feature flexible, schema-less designs, making them better suited for dynamic and rapidly evolving applications.
NoSQL and relational databases are not mutually exclusive; they complement each other and can coexist within the same ecosystem. An application can leverage different types of databases based on specific requirements and use cases, optimising performance, scalability, and functionality.