Week 9/33: Data Structures and Algorithms for Data Engineering Interviews
Understanding Fundamental Data Structures and Algorithms Practices
In Data Engineering interviews, coding assessments generally fall into two categories:
Real-World Coding Tasks – Practical problems involving data transformation, file handling, API integrations, and processing large datasets. These are commonly used in mid-sized tech companies, startups, and cloud-based data roles.
LeetCode-Style Algorithmic Challenges – Traditional Data Structures & Algorithms (DSA) problems, often used by large tech firms (FAANG, Fortune 500) in their screening rounds. These focus on optimising memory and computation efficiency and are typically part of online coding assessments.
While most companies now prioritise real-world problems, some big tech firms still assess algorithmic skills. That’s why understanding fundamental Data Structures and Algorithms is crucial for Data Engineers (if such companies are within our scope), even if the focus is more on practical applications than competitive programming.
What This Post Covers
This post focuses on essential Data Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions for Data Engineering Interviews, breaking down each question in a structured approach:
Thinking Steps – Understanding the problem, constraints, and approach
Solution Code – Writing an efficient implementation in Python
Explanation – Breaking down the logic, performance, and trade-offs
We’ll tackle real interview questions from big-tech companies like Amazon, Google, Meta, and Microsoft, focusing on scalable solutions relevant to Data Engineering workflows.
We will solve example questions to provide insight into what to expect in such rounds in Data Engineering interviews. However, the key to success is extensive practice and a deep understanding of programming fundamentals. Simply reviewing solutions is not enough, real improvement comes from solving problems independently, analyzing different approaches, and continuously refining problem-solving skills.
Topics Covered in This Post:
Arrays
Linked Lists
Stacks & Queues
Trees & Graphs
Sorting & Searching
For the previous posts of this series, check here: [Data Engineering Interview Preparation Series]1
Arrays
An array is a data structure that contains a group of elements of the same data type and stores them together in contiguous memory locations.
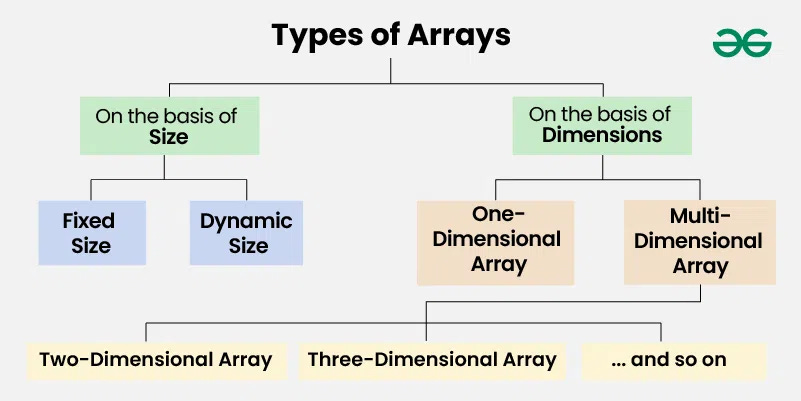
Arrays can be categorised based on size and dimensions:
1. Based on Size
Fixed-Size Arrays: Have a predefined size that cannot be changed after allocation. Memory is allocated either at compile-time or runtime.
Dynamic-Sized Arrays: Can grow or shrink during execution. Memory is allocated dynamically, allowing flexibility.
2. Based on Dimensions
One-Dimensional (1D) Arrays: A simple list of elements stored in a single row.
Two-Dimensional (2D) Arrays: Structured as rows and columns, like a table.
Three-Dimensional (3D) Arrays: A collection of 2D arrays, adding depth.
Arrays Interview Question by Meta2
Given a 2D array of user IDs, find the number of friends a user has. Note that users can have none or multiple friends.